Unveiling the Power of Ketosis: Why Should You Embrace It?
Ketosis is an inherent physiological process that takes place when the availability of glucose for energy is inadequate. Understanding how ketosis works and its potential benefits is essential.
Traditionally, carbohydrates have been regarded as the primary fuel source for our bodies, with the belief that we need them to function optimally. However, our bodies can generate an alternative fuel called ketones, which offer a cleaner and more efficient energy source.
If you're curious about determining whether your body is in a state of ketosis and the advantages it can bring, you may have some questions. In this comprehensive guide, you'll find answers to those queries and gain a thorough understanding of ketosis. So, let's delve deeper and continue reading to explore the topic in detail.

The Frequently Asked Question: What Exactly is Ketosis?
To truly understand the phenomenon of ketosis, it's essential to delve deeper into its workings. In most dietary situations, the body primarily relies on carbohydrates for energy. Carbohydrates, found in foods like grains, fruits, and starchy vegetables, are broken down into glucose during digestion. This glucose is then transported to the cells to be utilised as an energy source.
The body's capacity to store excess glucose comes into play when dietary carbohydrate intake exceeds immediate energy requirements. The surplus glucose is converted into glycogen and stored in the liver and muscles for future use. Glycogen is a readily available energy reserve that can be mobilised when needed.
However, the glycogen stores eventually deplete when you significantly reduce your carbohydrate intake, as with a ketogenic diet. Without an ample supply of glucose, the body must find an alternative fuel source to sustain its energy demands.
In this state of carbohydrate restriction, the body undergoes a remarkable metabolic shift. It starts to rely more heavily on fat as its primary fuel source. Adipose tissue, or body fat, becomes the main reservoir from which the body derives energy. The fat is broken down through lipolysis, resulting in the release of fatty acids.
As these fatty acids are further metabolised, the liver converts them into ketones through a process known as ketogenesis. Ketones, including acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone, can be utilised by various tissues and organs throughout the body as an alternative energy source.
The production and utilisation of ketones denote the state of ketosis. It is important to note that ketosis is a natural metabolic state that the body can enter and exit depending on dietary and physiological factors.
One of the remarkable aspects of ketosis is the potential benefits it offers. Many individuals report experiencing increased energy levels, enhanced mental clarity, and improved focus while in ketosis. Additionally, ketosis has been linked to appetite suppression, aiding weight loss.
Moreover, research suggests that ketosis may have therapeutic applications for conditions such as epilepsy, neurodegenerative diseases, and certain types of cancer. The precise mechanisms behind these benefits are still being investigated. Still, it is believed that the shift in fuel utilisation and the metabolic effects of ketones play a role in these positive outcomes.
By understanding ketosis and its impact on the body, you can better appreciate the potential advantages that a ketogenic diet or other approaches promoting ketosis may offer. It is important to note that adopting any significant dietary changes should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to ensure it aligns with your individual health goals and needs.
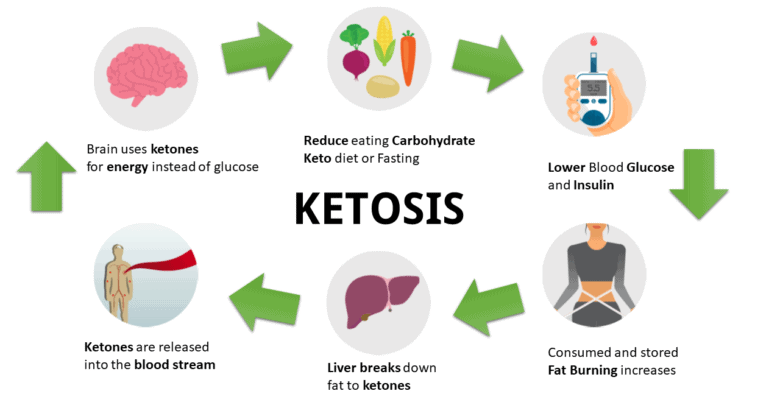
Is it Possible for Our Body to Rely on Ketones as the Primary Source of Energy?
The utilisation of ketones as the primary source of energy by our body is a somewhat nuanced concept. Let's explore the reasons behind this dual possibility:
Ketones, produced in the liver, can be transported from the liver to various tissues throughout the body. They possess the remarkable ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, allowing them to provide fuel for the brain, thereby serving as an alternative energy source for this vital organ. Moreover, our muscles readily utilise ketones as a significant energy substrate.
However, it is essential to acknowledge that specific tissues cannot utilise ketones effectively. Notably, our red blood cells (RBCs) and liver cells (hepatocytes) lack the necessary metabolic machinery to use ketones for energy production.
While the liver plays a crucial role in the production of ketones, it cannot harness their energy due to the absence of a specific enzyme required for their utilisation. The liver and red blood cells rely on a minimum amount of glucose for energy. To meet this requirement, a process called gluconeogenesis comes into play. The body synthesises glucose from non-carbohydrate sources through gluconeogenesis, ensuring the liver and red blood cells receive the necessary glucose for optimal functioning.
This unique interplay between ketones and glucose highlights the intricacies of our body's energy metabolism. While ketones can serve as an alternative fuel source for various tissues, the reliance on glucose remains vital for specific cells and organs.
Understanding the complexities of energy metabolism aids in appreciating the dynamic relationship between ketones and glucose within our body's physiological processes.
Exploring the Differences: Ketosis vs. Ketoacidosis
It's not uncommon for confusion to arise when distinguishing between ketosis and ketoacidosis. While the terms sound similar, they are distinct metabolic states with different implications for our health.
Ketosis, in its essence, is a natural metabolic process that occurs when our body shifts its primary energy source from glucose to ketones. When we consume fewer carbohydrates, our liver begins to break down stored fat into molecules called ketones. These ketones are then used by various tissues and organs, such as the brain and muscles, as an alternative fuel source. Ketosis is often achieved through a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet, such as the ketogenic diet, or during periods of fasting.
On the other hand, ketoacidosis is a potentially dangerous condition that arises when the production of ketones becomes excessive and uncontrolled, leading to a significant imbalance in the body's acid-base equilibrium. Ketoacidosis is most commonly associated with individuals who have type 1 diabetes, although it can occur in those with type 2 diabetes as well. This condition usually occurs when there is a lack of sufficient insulin to regulate blood sugar levels properly. Without enough insulin, the body cannot effectively utilise glucose for energy, prompting it to produce ketones excessively. As a result, both ketone levels and blood sugar levels rise to dangerously high levels, exceeding 240 mg/dl. Factors such as missed insulin doses, increased stress, or excessive alcohol consumption can trigger ketoacidosis.
It is crucial to note that while ketosis is a natural metabolic state that is generally safe and desirable for many individuals, ketoacidosis is a medical emergency requiring immediate attention and intervention. The two conditions should not be confused or equated with one another.
To better understand and differentiate between ketosis and ketoacidosis, exploring their causes and symptoms is essential. By gaining a more profound comprehension of these metabolic states, we can navigate the complexities of our body's energy metabolism and make informed decisions about our dietary choices and overall health.

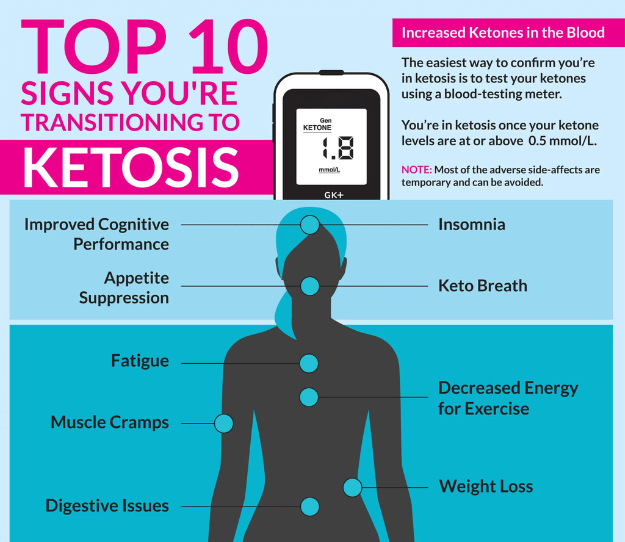
Detecting the Signs of Ketosis: How to Know if You're in Ketosis
Having a clear understanding of what ketosis entails, it becomes crucial to recognise the telltale signs that indicate you have entered this metabolic state. Without being aware of the common symptoms associated with ketosis, it's easy to mistake them for flu-like symptoms or unrelated discomforts.
If you experience any of the following symptoms, there's no need to panic. They are typically a result of your body's transition from relying on carbohydrates as its primary fuel source to becoming adept at burning fats for energy.
-
Ketosis Breath - One distinctive sign of ketosis is the presence of what some refer to as "ketosis breath." This peculiar breath has an odour similar to nail polish remover, which can be attributed to the release of a ketone called acetone. Interestingly, acetone in the breath can be a reliable indicator of ketosis. Don't worry; in most instances, keto breath lasts only weeks and can be masked with good oral hygiene and some gum!
-
Ketosis Strips - Another method to gauge ketosis is using urine-based ketosis strips. These paper strips help determine the presence of ketones in your urine. As your body eliminates ketones through urine, these strips offer a convenient and accessible means of assessing your ketone levels.
-
Weight Loss - Low-carbohydrate diets, including the ketogenic diet, are renowned for their effectiveness in promoting weight loss. Research has shown that a ketogenic diet can lead to more significant weight loss than low-fat diets. When first embarking on a ketogenic journey, you may notice a significant initial drop in weight, primarily due to losing water weight.
-
Short-Term Fatigue - It is not uncommon for individuals new to the ketogenic diet to initially experience fatigue and decreased performance. However, it's important to remember that these symptoms are typically transient. As your body adapts to using fats for fuel, you can expect your energy levels to rebound, increasing your vitality.
-
Appetite Suppression - Ketosis has been found to suppress appetite, naturally contributing to weight loss. The mechanisms behind this effect may include the impact of ketosis on appetite-regulating hormones or the modulation of gut microbiome activity.
For those embarking on their ketogenic journey, it's essential to recognise that any negative symptoms experienced during the early stages are generally temporary and subside as your body adapts to its new energy source.
In addition to the symptoms mentioned, other potential indicators of ketosis are worth noting. This guide will further explore these symptoms and provide simple strategies to manage them effectively. By familiarising yourself with these signs, you can gain greater confidence in identifying and harnessing the benefits of ketosis.
Unveiling the Health Benefits of Ketosis
One may naturally wonder about the impact of ketosis on overall health and well-being. Is it genuinely advantageous for the body to be in a state of ketosis?
Ketosis, a normal metabolic state, offers a range of benefits for healthy individuals and those at risk of certain conditions.
-
Weight Loss - It is no surprise that weight loss is a prominent benefit of nutritional ketosis. Shedding excess pounds through a ketogenic approach positively affects various aspects of life. Even a modest weight loss of just 5% can lead to reduced inflammation, decreased cancer risk, and lower triglyceride levels.
-
Cardiovascular Health - Research suggests that nutritional ketosis may improve cardiovascular health. Human studies have shown associations between ketosis and lower total cholesterol levels, increased levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol (often referred to as "good" cholesterol), and reductions in low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and triglycerides. These factors collectively improve cardiovascular risk profiles.
-
Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes - By maintaining blood glucose levels within a low and normal range, the ketogenic diet may help reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Moreover, evidence from a non-randomised trial spanning two years indicates that long-term nutritional ketosis can even lead to the reversal of the condition.
-
Brain Health and Mental Clarity - The ketogenic diet, initially employed in the 1920s as a treatment for epilepsy, has demonstrated beneficial effects on brain health. The diet offers neuroprotective benefits by providing an alternative energy source for the brain in the form of ketones. Many individuals report increased focus, improved memory, and enhanced brain function while in ketosis.
-
Prevention of Metabolic Diseases - Carbohydrate restriction, a vital aspect of the ketogenic diet, has improved multiple components of metabolic syndrome. These include weight management, fasting blood sugar, triglyceride, HDL cholesterol, and blood pressure. By addressing these factors, a ketogenic approach can help prevent the development of metabolic diseases.
For a more comprehensive understanding of how a ketogenic diet brings about these benefits, this guide delves deeper into the underlying mechanisms and explores additional advantages. By examining the potential advantages of ketosis, you can make informed decisions about your dietary choices and lifestyle to promote optimal health and well-being.

Accelerating Ketosis: Strategies to Enter Ketosis Quickly
If you're looking to expedite the process of entering ketosis, there are several practical approaches to consider:
-
Reduce Carbohydrate Intake - The first step is to minimise your reliance on carbohydrates for energy. Aim to limit your daily carbohydrate intake to 20-50 grams. For a more personalised approach, utilising a keto calculator can help you determine your ideal macronutrient ratios.
-
Increase Healthy Fat Consumption - As you decrease your carbohydrate intake, you must compensate by increasing your consumption of healthy fats. Incorporate sources such as MCT oil, avocados, fatty fish, nuts and seeds, whole eggs, and olive oil into your diet. Avoid fats from processed foods, as they can hinder your progress.
-
Implement Intermittent Fasting - Intermittent fasting can play a significant role in expediting the onset of ketosis. While fasting may not suit everyone, it depletes your glycogen stores, prompting your body to tap into its fat reserves and produce ketones.
-
Boost Physical Activity - Engaging in high-intensity workouts can hasten the transition into ketosis, particularly when combined with a low-carbohydrate diet and intermittent fasting. Physical activity helps deplete glycogen stores and accelerates the body's utilisation of fats for fuel.
For a more comprehensive exploration of the steps involved in entering ketosis, including additional strategies and detailed guidance, please look at the complete information provided in this guide. By following these approaches, you can optimise your chances of swiftly achieving the state of ketosis.

Intermittent Fasting and the Keto Diet: Accelerating Weight Loss and Staying Healthy
When starting the keto diet, incorporating fasting practices can amplify the benefits of this low-carbohydrate, high-fat eating approach. Fasting on the keto diet not only promotes faster weight loss but also offers additional health advantages. However, it's essential to approach fasting with caution and prioritise your well-being. Here are some best fasting practices to consider when embarking on the keto diet and tips for maintaining good health during fasting:
-
Start gradually: If you're new to fasting, it's best to ease into it gradually. Begin with intermittent fasting, which involves restricting your eating window to a specific period, such as 16 hours of fasting followed by an 8-hour eating window. As your body adjusts, you can experiment with longer fasting periods.
-
Stay hydrated: It's crucial to stay hydrated during fasting periods. Drink plenty of water, herbal tea, and electrolyte-rich fluids to maintain proper hydration and support your body's functions.
-
Ensure nutrient balance: While fasting, it's essential to prioritise nutrient-dense foods during your eating window. Focus on incorporating high-quality proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of low-carbohydrate vegetables to provide essential vitamins, minerals, and micronutrients.
-
Listen to your body: Pay attention to your body's cues and adjust your fasting routine accordingly. If you feel excessively fatigued or experience discomfort, consider shortening the fasting window or consulting a healthcare professional for guidance.
-
Monitor electrolytes: As you transition into ketosis and fasting, your body excretes more water and electrolytes. To maintain proper electrolyte balance, consider supplementing with magnesium, potassium, and sodium or consuming foods rich in these minerals.
-
Prioritise sleep and stress management: Adequate sleep and stress management are crucial for overall health. Aim for quality sleep and engage in stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to support your well-being during fasting periods.
-
Be mindful of your energy levels: Fasting can, at first, cause a dip in energy levels as your body adapts to using fat for fuel. Take it easy during this adjustment period, and allow yourself ample rest and relaxation.
-
Focus on whole foods: During your eating window, emphasise whole, unprocessed foods that align with the principles of the keto diet. This response includes incorporating healthy fats, lean proteins, non-starchy vegetables, and small amounts of low-carbohydrate fruits.
By incorporating fasting into your keto journey and following these best practices, you can accelerate weight loss while maintaining good health. However, it's crucial to listen to your body, prioritise your well-being, and consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making any significant dietary changes or engaging in fasting practices, especially if you have underlying medical conditions.

Are There Any Adverse Effects of Ketosis on Your Health?
In an ideal scenario, being in a state of ketosis should benefit your overall health. However, it's essential to acknowledge that specific side effects can accompany the transition into ketosis. It's worth noting that these effects are typically temporary and can vary in duration based on individual adjustments to the new diet.
Common side effects of entering ketosis may include fatigue, bad breath, headaches, insomnia, gastrointestinal issues such as diarrhea or constipation, and potential changes in cholesterol levels. These symptoms generally subside within a few days to a month as your body adapts to the ketogenic diet.
You can refer to the detailed guide on this subject for a more comprehensive understanding of the potential side effects associated with ketosis.
While ketosis can benefit many individuals, it is crucial to recognise that the diet may not suit everyone, particularly in certain medical conditions. Individuals with conditions such as pancreatitis, fat metabolism disorders, or liver failure should avoid the ketogenic diet due to potential complications.
Breastfeeding women should exercise caution as carbohydrate restriction can sometimes lead to ketoacidosis. Following a ketogenic diet during pregnancy and lactation is generally not recommended, as these periods require specific nutritional considerations.
In summary, if you are uncertain whether the ketogenic diet is appropriate for you, it is essential to consult your healthcare provider, especially if you have an underlying medical condition or are taking medications. Their expertise will help you make an informed decision and ensure your safety and well-being throughout the dietary journey.

Key Points to Remember
In summation, here are the key takeaways regarding ketosis:
-
Ketosis occurs when your body utilises fats for energy instead of glucose. Strategies such as reducing carbohydrate intake, engaging in physical activity, and practising intermittent fasting can expedite the process. It is essential to increase healthy fat consumption during this metabolic state.
-
When entering ketosis, it is common to experience temporary side effects lasting from a few days to a month. These symptoms include fatigue, bad breath, headaches, insomnia, and potential gastrointestinal issues. They are typically part of the body's adjustment process.
-
Ketosis has been found to have positive impacts on various aspects of health. Research indicates it can benefit heart health, weight management, brain health, blood glucose control, and overall metabolic health.
-
It is important to note that while ketosis benefits many individuals, it may not be suitable for everyone. Before embarking on a ketogenic diet or significant dietary changes, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian. They can provide personalised guidance and ensure it aligns with your health needs and circumstances.
By being well-informed and seeking professional advice, you can make informed decisions about incorporating ketosis into your lifestyle and maximise its potential benefits.






































